Problem: Given an integer array nums where the elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height-balanced binary search tree.
A height-balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than one.
Example 1:
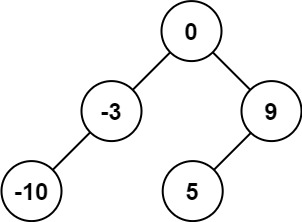
Input: nums = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: [0,-10,5,null,-3,null,9] is also accepted:
Example 2:
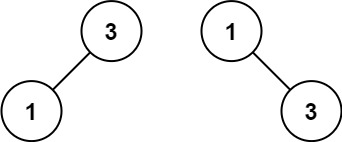
Input: nums = [1,3] Output: [3,1] Explanation: [1,3] and [3,1] are both a height-balanced BSTs.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104numsis sorted in a strictly increasing order.
This problem is popular in LeetCode and GeeksForGeeks A collection of hundreds of interview questions and solutions are available in our blog at Interview Question
Solution
No comments:
Post a Comment