Problem: Given the root of a binary tree, the value of a target node target, and an integer k, return an array of the values of all nodes that have a distance k from the target node.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
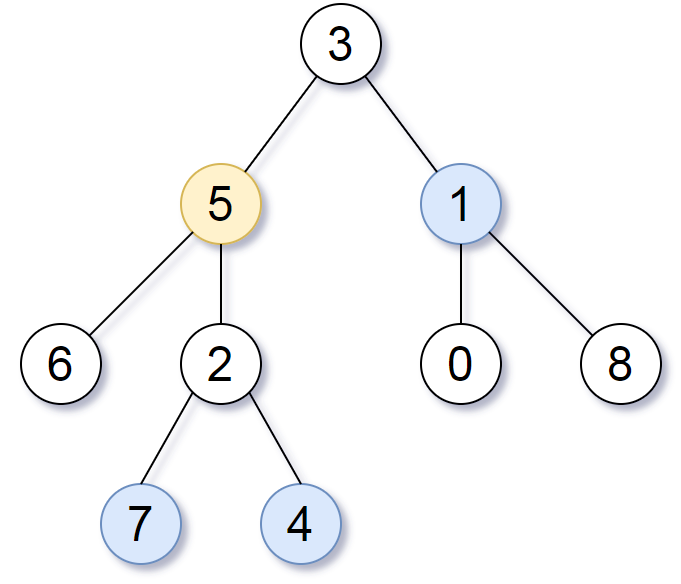
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, k = 2 Output: [7,4,1] Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 1, k = 3 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- All the values
Node.valare unique. targetis the value of one of the nodes in the tree.0 <= k <= 1000
This problem is popular in LeetCode and GeeksForGeeks. A collection of hundreds of interview questions and solutions are available in our blog at Interview Question
Solution:
No comments:
Post a Comment